What is a Torn Meniscus?
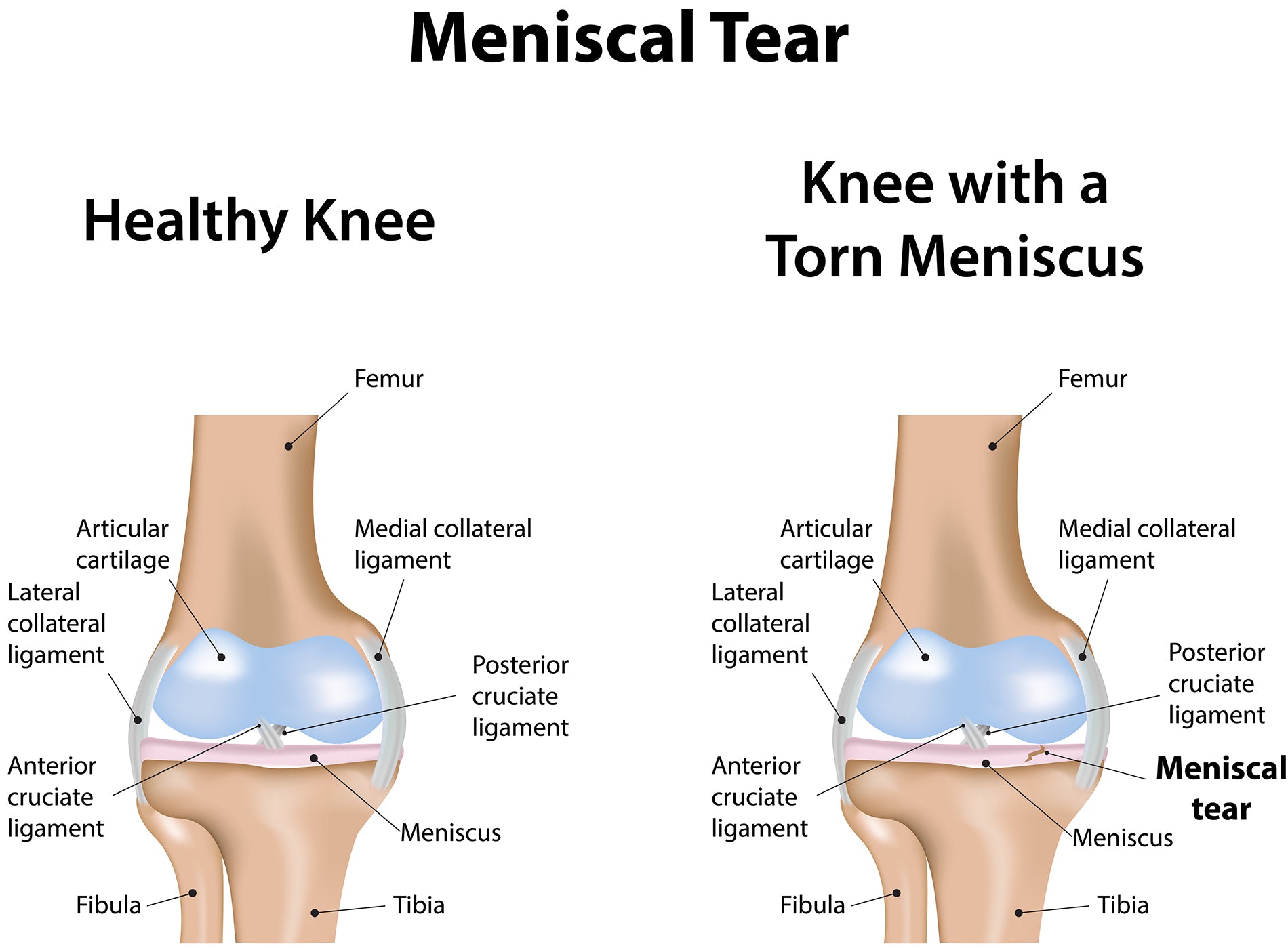
The knee joint is made up of three bones: the patella (kneecap), the shinbone(tibia), and the thighbone (femur). In addition, two wedged pieces of cartilage in the shape of kidneys are located between the femur & tibia. These are called menisci and cushion the knee, provide stability, and protect the joint.
Damaged menisci can no longer absorb impacts and allow for smooth movement. A torn lateral meniscus is on the outside of the knee, while the medial meniscus is in the knee's inner part.
There are many types of Meniscus Tears.
Menisci injury is classified based on appearance and geographic location. Here are the various types of meniscus tears.
Flap Tear
This injury occurs on the meniscus side. It results in a flap when the inner tissues split away from the edge.
Degenerative Tear
Degenerative tears are caused by injury to the menisci, which causes gradually more significant damage around the outside of the meniscus.
Acute Tear
The sudden injury of the meniscus is caused by forceful bending or twisting of the knee. It is more common during sports.
Bucket Handle Tear
A bucket handle tear separates the meniscus' outer edge and inner tissue. The bucket handle shape forms when the meniscus' edge is separated from the rest, and the cartilage and the torn piece lift.
Radial Tear
This type of tear causes damage to one side of the meniscus. It then spreads into the tissue, which is perpendicular to that edge.
Torn Meniscus Causes
What causes a torn meniscus? The most common cause of meniscal tear is a traumatic injury. However, the causes of meniscal tears will guide your treatment decisions.
Sports Injury
Sudden meniscus tear, partial or complete, is most common during sports. A direct impact to the knee's front or side forces the joint to move in the opposite direction. Also, forceful bending, twisting, and direction changes can cause injury. These lead to a menisci tear or anterior cruciate ligament ( ACL) tear.
Degenerative joint conditions
After 50, knee injuries can be more easily linked to degenerative joint conditions such as osteoarthritis. OA can also cause a meniscus tear. OA can cause the cartilage in the meniscus to wear unevenly and become less flexible and resilient, making it easier to tear.
Repetitive movements
The cartilage of the knee is affected by age. Bad form, such as squatting constantly or stepping on uneven ground, can cause knee injury. Tears are more common in worn, old, or imbalanced tissues. A torn meniscus may result from a sudden turn or a wrong twist in getting up from the chair.
Torn Meniscus Symptoms
Meniscus tears can cause symptoms that vary depending on the location of the tear, how long it has been since the injury and your overall health. The following are common symptoms of a torn Meniscus:
Swelling
This is caused by fluid accumulation at the knee joint. You will feel less mobility if the entire area becomes stiffened and swollen. It is often called "water in your knee."
Pain
The location of the tear is usually easy to spot with palpation. However, the pain can often spread throughout the knee when there is movement. Rotating or twisting the knee can cause intense pain.
Clicking or Popping Sensation
Depending on how torn it is, a piece of the meniscus might come off and be able to move into the joint. A snapping or popping sensation is common with meniscus tears. Sometimes, the patient may feel the knee giving out.
Knee locking
You feel like your knee is locked when you move it. If a meniscus fragment is ripped from the disc structure, it can be difficult to straighten your leg while standing or sitting.
Diagnosis for Torn Meniscus
To determine if your knee pain is due to a torn or damaged meniscus, consult your doctor. Before recommending the best treatment for you, your doctor will assess the extent of the injury and determine which meniscus is damaged. These methods will help your doctor diagnose a torn meniscus.
1. Medical History
Your doctor will ask you about your medical history, including the onset of the injury, whether it was over-rotated in the knee if there was a popping sound, and whether there was pain immediately.
2. Physical Examination
Your doctor will move your leg in various directions to assess your range of motion. This will determine if the tear is from the medial or the lateral meniscus. They might also examine the lower body for swelling and strength.
3. MRI Scan
Your doctor may order a magnetic resonance imaging scan (MRI) to determine the severity, size, and location of the meniscal tear. It all depends on how severe your symptoms are. This diagnostic test shows clear images of the soft tissue in the knee joint. What does a torn Meniscus look like? An MRI will help you see. An MRI will show your doctor if there are any tears in the meniscus or excess fluid.
Treatment
Treatment for a meniscus tear depends on the severity of the tear and your individual needs. Most people with meniscus tears can be treated with non-surgical methods, such as:
- Rest. Avoiding activities that aggravate your knee pain can help reduce inflammation and give your meniscus time to heal.
- Ice. Applying Cold therapy pack to your knee for 20 minutes at a time, several times a day can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Compression. Wearing a compression bandage or sleeve can help to reduce swelling and pain.
- Elevation. Raising your leg above the level of your heart when sitting or lying down can help reduce swelling.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help relieve pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy. A physical therapist can teach you exercises to strengthen the muscles around your knee and improve your range of motion.
If non-surgical methods are ineffective, your doctor may recommend surgery to repair the torn meniscus. There are a number of different surgical procedures that can be used to repair a meniscus tear, depending on the location and severity of the tear.
Preventing Meniscus Tear
There are a number of things you can do to prevent meniscus tears, including:
- Warm up before exercise. Warming up helps to prepare your muscles and tendons for activity, which can help to reduce your risk of injury. A good warm-up should include some light cardio, such as jogging or jumping jacks, followed by dynamic stretches, such as leg swings and lunges.
- Stretch regularly. Stretching the muscles in your legs, especially your thighs and hamstrings, can help to improve flexibility and reduce your risk of injury. It is important to stretch after exercise as well as before.
- Strengthen the muscles around your knee. Strong muscles around your knee can help to support the knee joint and reduce the risk of injury. You can do several exercises to strengthen the muscles around your knee, such as squats, lunges, and leg raises.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of meniscus tear.
- Wear supportive shoes. Wearing supportive shoes can help to reduce stress on your knees and ankles. When choosing shoes, look for shoes with good arch support and a cushioned sole.
- Avoid overuse. If you experience pain in your knee, stop the activity and rest. Continuing the activity could make the injury worse.
Consider wearing a knee brace if you are active in sports or other activities that stress your knees. Knee braces can help to support the knee joint and reduce the risk of injury.
Here are some additional tips for preventing meniscus tears:
- Use proper lifting techniques. When lifting heavy objects, bend at the knees, not the waist. This will help to reduce stress on your back and knees.
- Avoid sudden movements. Sudden movements like twisting or rotating your knee can increase your risk of developing a meniscus tear.
- Be aware of your surroundings. When walking or running, be aware of uneven surfaces and obstacles that could cause you to trip or fall.
If you have any concerns about meniscus tears, talk to your doctor.
Torn Meniscus Recovery Time
It takes six to eight weeks for a torn meniscus to heal completely. It all depends on the method you use to treat your injury. It is always a good idea to begin physical therapy. Before you can resume your normal activities, you must restrain your movement for at least two weeks.
Getting a diagnosis early and using the correct treatment methods like rest, physical therapy, heat with Sacksythyme's Everywhere Microwaveable Heating Pad, and Cold therapy with a cold therapy pack is important to recover fully. As you return to daily life, be sure to follow your doctor's orders. To prevent injury from happening again, you should continue to visit your doctor. A high-quality knee brace protects your knees and maintains a healthy joint.